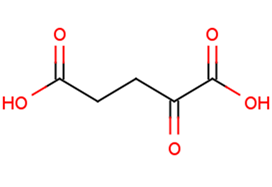
2-Ketoglutaric acid
CAS No. 328-50-7
2-Ketoglutaric acid( —— )
Catalog No. M20576 CAS No. 328-50-7
2-Ketoglutaric acid is a key molecule in the tricarboxylic acid cycleis also connected to glutamic acid and glutamine metabolisms through the transamination reactions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1G | 38 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Ketoglutaric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Ketoglutaric acid is a key molecule in the tricarboxylic acid cycleis also connected to glutamic acid and glutamine metabolisms through the transamination reactions.
-
Description2-Ketoglutaric acid is a key molecule in the tricarboxylic acid cycleis also connected to glutamic acid and glutamine metabolisms through the transamination reactions.
-
In Vitro2-Ketoglutaric acid (Alpha-Ketoglutaric acid) has other physiological capabilities including reduction of ammonia level formed in the lung and general ammonia detoxification, protective role against lipid peroxidation and neuroprotective effect against cyanide poisoning.2-Ketoglutaric acid acts as precursor for the synthesis of amino acids and nucleotides.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number328-50-7
-
Formula Weight146.1
-
Molecular FormulaC5H6O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:50 mg/mL (342.23 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESOC(=O)CCC(=O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Glucagon-Like Peptid...
Glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) is a recently identified intestinal epithelium-specific growth factor that has been shown to reduce the severity of inflammatory disorders of the intestine in rodent models. Currently Glucagon-Like Peptide 2 is used as a potential therapeutic agent for the human subjects with a broad variety of intestinal diseases characterized by intestinal damage and insufficiency.
-
Indole-3-acetamide
1H-Indole-3-acetamide also known as auxin amide or 2-(3-indolyl)acetamide belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 3-alkylindoles. Within the cell 1H-indole-3-acetamide is primarily located in the cytoplasm. 1H-Indole-3-acetamide can be biosynthesized from acetamide.
-
N1-Acetylspermidine ...
N1-Acetylspermidine hydrochloride, an acetyl derivative of spermidine, serves as a substrate for polyamine oxidase and selectively elevates its levels in human colorectal adenocarcinomas.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


